...
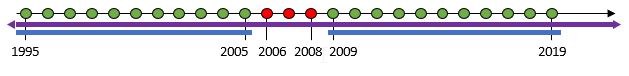
The availability of these positions in this dataset can be visually represented as such:
The selection mode determines, for each dimension, which positions are taken into account (and therefore displayed in the Data Browser), and which positions are not taken into account (and therefore hidden from the Data Browser).
...
Always all positions: In this mode, all the positions made available in the dataset for this dimension will be taken into account. Applied to the provided example, this will select the following positions:
From 1995 to 2005
From 2011 to 2019
Evolution through time: It is important to understand that using this selection mode means that every position added in the future (by the agency which manages this dataset), for this dimension within this dataset, will also be taken into account in the selection. So, for example, if the agency retroactively publishes data for this dataset for years 2009 and 2010, the following positions will be selected, using this selection mode:
From 1995 to 2005
From 2009 to 2019
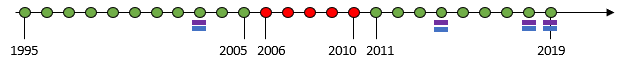
Static positions: In this mode, only the positions specifically checked will be taken into account in the selection. So, for example, assume that the following positions are checked:
2003
2014
2018
2019
Only those positions will be taken into account in the selection. If other positions are added in the future in this dataset, those new positions will not be present in the selection.
Fixed time (this selection mode is available only for the Time dimension): In this mode, the selected positions for the Time dimension will match a timespan which is manually defined by selecting “Last X time” from the drop-down. The end of the timespan matches the current time and the beginning is automatically set by counting down to the X time set. All the available positions located inside the interval will be present in the selection. So, for example, if selecting “Last 10 Time” with the provided example, the selected positions will be:
2005
From 2011 to 2019
Using this selection mode, the selection might be impacted by retroactive actions on positions availability:
If positions which are inside the selected timespan interval (for example 2009 and 2010) are retroactively added, 2010 will be added and 2005 will be removed from the selection;
If new position is added to the Time dimension (in other words, the most recent data is added to the dataset), the selection will be modified to reflect the change: this new position will be added to the selection and the oldest year will be removed.
...
From-To (this selection mode is available only for the Time dimension): In this mode, the selected positions for the Time dimension will match a timespan interval, for which the beginning and the end are manually defined. All the available positions located inside this interval will be present in the selection. So, for example, if selecting “From 2002 to 2014” with the provided example, the selected positions will be:
From 2002 to 2005
From 2011 to 2014
Using this selection mode, the selection might be impacted by retroactive actions on positions availability:
If positions which are inside the selected timespan interval (for example 2009 and 2010) are retroactively added, these positions will be added to the selection;
If the retroactively added positions are located outside of the selected timespan interval, these added positions won’t affect the selection.
Rolling Time (this selection mode is available only for the Time dimension): In this mode, the selected positions for the Time dimension will match a timespan for which the beginning is manually defined. The end of the timespan matches the current time. All the available positions located inside this interval will be present in the selection. For example, if selecting as beginning the 2004 position, the selected positions will be:
2004 and 2005
2011 up to now (“now” has to be understood as the time when the dataset is browsed in the Data Browser)
Using this selection mode on a dataset will likely have an impact on the selected positions over time: indeed, each time a new position is added to the Time dimension (in other words, each time the most recent data is added to the dataset), this new position will be added to the selection.
...
This process is described in detail on this page.